Remote access to an environment is extremely useful. However, it also brings security risks. Without tuned-up control over the remote desktop, any user exposes its sensitive data and connected devices to danger, let alone businesses, for whom fully protected remote environments have become a must.
Have you secured your sessions with a password system? Unfortunately, today’s hacking methods can cope with practically any. This is where the biometric access control approach comes in handy.
How do biometrics work? What are the advantages of these security methods for remote desktop environments? How to integrate a reliable multi-factor authentication system into RDP sessions? All answers are in the blog below.
The Essence of Biometrics
A biometric login to a system or account is based on providing a human’s physical or behavioral authenticator or a combination of them to withstand identity control. Let’s overview the physical metrics first:
- Face recognition.
- The fingerprint method.
- Finger’s geometry scanning.
- Voice recognition.
- Reading a user’s retina or iris data.
- DNA.
- Ear shape scanning.
- Vein recognition.
- Odor recognition.
Behavioral authenticators are based not only on physiological parameters but also on those related to unique human habits and activities. They represent a smaller group:
- Signatures.
- Keystroke checks.
- Gait recognition.
Some of these methods have become mainstream in certain domains, while others may still seem strange and too complex for mass usage. However, all of them have one undeniable advantage over good old logins and passwords — they are unique and hard to steal.
Why Is Remote Desktop Security Crucial?
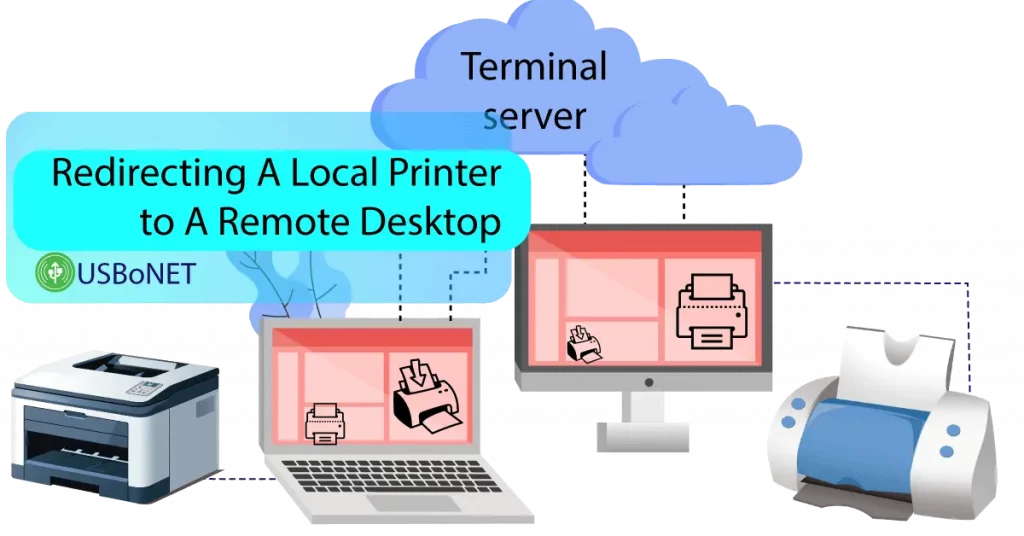
Today’s eCommerce projects and online business challenges require a unified environment with remote access to a scanner, printer, or any other device. Users might need to redirect access to both peripheral gadgets and information.
Tuning up such an environment does not only mean creating a workable remote desktop configuration. Its must-have components include security settings. Without them, unauthorized access to peripherals and data may cause significant damage.
How Biometrics Help with RDP Security
The introduction of biometric authentication provides a higher level of security for desktop systems with distant users connected via USB, Ethernet, WiFi, etc. Cybercriminals can hack digital passwords using malware software. The worst thing is that they can even break in via various plugins employed by users on their remote desktops!
With login security based on biometrics, we receive an environment to which a user can sign in only after they provide their physical parameters. Hacking or stealing them is an almost impossible undertaking.
Remote Desktop Access: Popularity Growth & Challenges
Networks of computers connected to a host workstation that provide users with access to devices and data from any distance are no longer attributes of Sci-Fi fiction. The lockdowns of 2020 provoked a rise in eCommerce and remotely working offices. Most businesses soon understood how profitable such an approach can be.
Challenges in Traditional Authentication Methods
For modern technologies, it’s not a problem to virtually connect the broadest set of devices. Exchanging data is also available via various solutions. What still represents a challenge is secure access management. Commonly used passwords and PIN codes cannot guarantee proper protection anymore due to the following problems:
- Passwords can be stolen in multiple ways.
- Users may lose their passwords.
- Users may share their passwords by mistake.
What does it mean? Surely, the use of remote desktop environments will continue to grow by all means. However, they need new methods of authentication, and biometrics can provide effective solutions.
How Biometrics Are Captured & Stored
At present, there’s a range of specialized software designed for the full management of biometrics for secure remote access. In simple words, it works like this:
- A user’s ‘bio’ data is captured with the help of specific scanners (voice readers, iris scan programs, fingerprint detectors, etc.).
- The data is transformed into so-called templates.
- Biometric templates are stored on hardware, smartphones, or biometric servers. The latter is rather hackable. The most reliable way to store biometrics is in the form of portable tokens.
- The user logs in, providing their fingerprints, retina, or another physical/behavioral metric, and the system compares his data with the one stored.
Thus, users enter the virtual desktop environment. Unauthorized logging in is, at least, extremely challenging. When used in combination with a password system or another security method, such biometrics-based multi-factor authentication is practically unhackable.
Advantages of Biometrics
The benefits of biometric login systems are listed below:
- You cannot forget your fingerprints or retinas.
- You do not need to remember anything.
- No one can steal a user’s biometrics unless serious damage is caused to their health.
- General convenience.
Multi-factor login systems are easy to integrate into desktop environments. There are universal solutions for collecting, storing, and verifying physical data for Windows, Linux, and other OSes. Users can expect seamless experiences with such software.
Best Practices for Deploying Biometric Authentication
Without smooth integration with a company’s hardware, software, and employees, the best software for remote desktop security will fail. So, it is crucial to tune up your biometric authentication system by applying the following first-priority rules:
- Combine login methods. Yes, biometrics are almost unhackable. Still, the best approach to RDP security is to employ two-factor authentication.
- Encryption of a modern type should be used for collecting, processing, and storing biometrics.
- System accuracy is the first thing to check. It’ll protect your remote sessions against false recognition experiences.
- Updates are a must for your biometric login firmware. Keeping all software and drivers up-to-date will prevent fraudsters from finding even the smallest loophole.
- System audits should also be regular. You need to ensure that your biometric login system works properly and that all employees can sign in seamlessly.
- Clear procedures are necessary to simplify the usage of biometrics for all authorized users on remote desktops.
- Regular training is a great option for employees.
The main challenge here is ensuring correct data recognition. Customers may create irrelevant templates during physical data captures, which will lead to false negatives in the future. On the other hand, if the system detectors work improperly, false positives are also possible.
So, it’s crucial to employ industry-grade biometric recognition software. Another priority is to train employees to use the system correctly.
Regulatory & Ethical Considerations
Private data regulations are implemented in many countries worldwide. Examples include the EU GDPR Policy and Australia’s Privacy Act. However, these laws are still being formed. Since we have just started using biometric authentication and similar online activities, updates and applications to such regulatory policies are required.
On the other hand, users may worry about their physical data capture for a number of reasons. They may be anxious about attempts of unethical data collection. The fear of hacking is also natural since scammers do not stop inventing their ‘lockpicks’, too. However, this uneasiness can be overcome by providing simple and secure login systems with training courses and explanatory demonstrations.
Conclusion
Biometrics seems to take a key position in every login system on remote desktops. When used with another security method, it can be untouchable for any sort of attack. Certified equipment and enough transparency make up a perfect formula for your business, and your employees will be able to log in remotely, hands down, without security concerns.